I usually use Google BigQuery only for simple aggregate SQL, but there are many other useful functions besides aggregate SQL.
However, since I don't use it often and when I do try to use it, I start by looking for a manual, so I'm going to put together a brief description of how to use it for myself.
Here is a summary of the scheduled queries.
Scheduled queries
- It executes the specified query at the specified date and time and writes it to the specified table.
- The date and time of execution can be passed to the query as a parameter
- Can be run retroactively.
Cannot call other scheduled queries sequentially
- Can't build a pipeline.
Execution time parameters are not available in the console
- Unable to check query behavior in console
Example
Runtime Parameters
- Time when
@run_timewas executed (UTC) Date of
@run_dateexecution (UTC)- Rarely used if working in local time.
- Time when
SELECT @run_time AS query_run_time_utc, @run_date AS query_run_date_utc
Writing to the read time table
- If
${run_time|"%Y%m%d"}is appended to the end of the table, it will be written to the execution date partition.
Example
Write to yesterday's partition in JST
+9 (JST) - 24 (yesterday) = -15
- Write to a date partition of "Execution date - 15 hours".
table_name${run_time-15h|"%Y%m%d"}
- Overwrite table

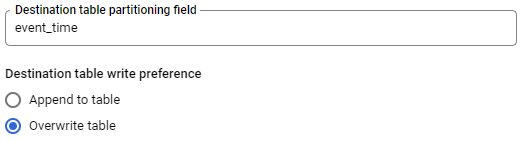
Writing to the partition table
- Specify partitioning fields
- Overwrite table
Other
Cannot call other scheduled queries sequentially
- Can't build a pipeline.
Execution time parameters are not available in the console
- Unable to check query behavior in console
Because of these specifications, they are not very user-friendly.
As an alternative to sequential execution, prepare a query that performs equivalent "query execution and table writing" and call the query from a stored procedure that takes a time argument. Then, from the scheduled query, call the stored procedure with @run_time as an argument.